Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule? - Dna Base Pairs Overview Structure Expii - Across the nitrogenous bases, they form between the complementary base pairs thymine and adenine and also cytosine and guanine.
Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule? - Dna Base Pairs Overview Structure Expii - Across the nitrogenous bases, they form between the complementary base pairs thymine and adenine and also cytosine and guanine.. Which pair of nitrogen bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? Dna is composed of two strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonding. Each nucleotide unit has a nitrogen containing base. In a dna sample, the percentage of adenine is 40% and percentage of thymine is 60%. Deoxyribonucleic acid, more commonly referred to as dna, is the primary genetic material for almost all life.
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning. This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern: The possibility of adenine=40% and. The nitrogenous bases stacked upon one another are spaced based on their van der waals distance. In a dna molecule, adenine and thymine bases always pair up, and cytosine and guanine always form hydrogen bonds form between the nitrogenous bases in a dna molecule.
Iii according to the gels.
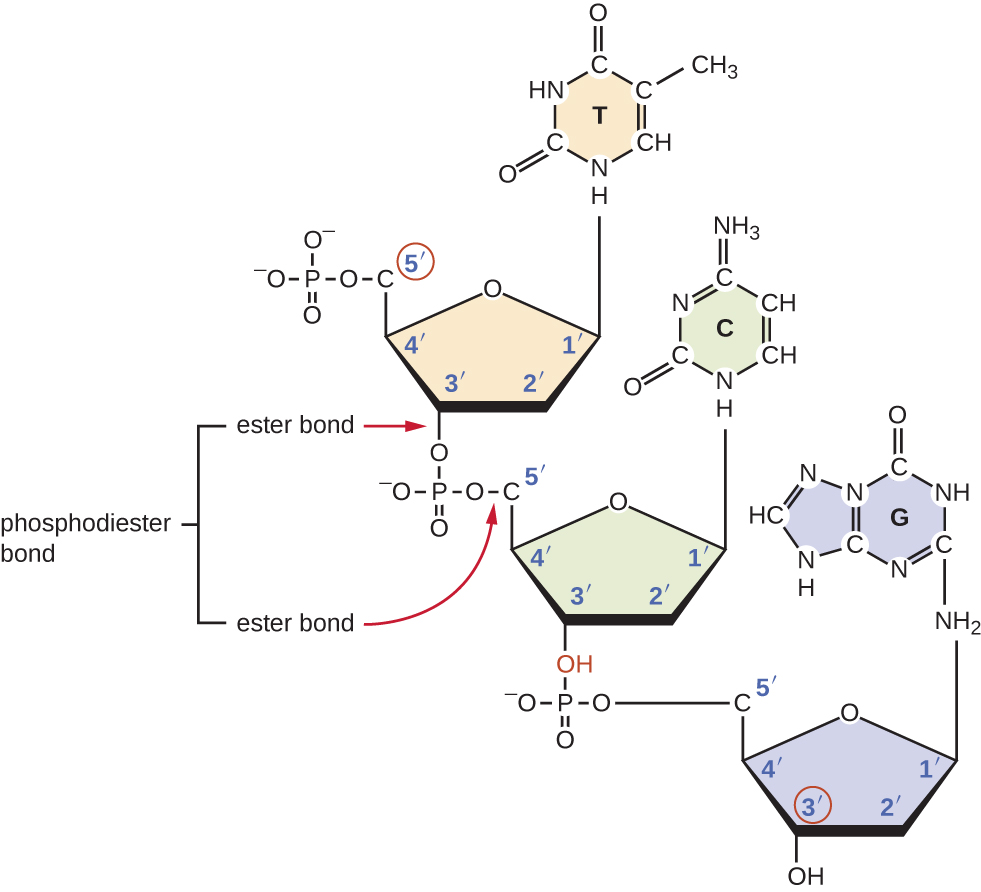
The possibility of adenine=40% and. Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid which is a molecule that contains the instructions an there are 4 types of nitrogen bases adenine (a) thymine (t) guanine (g) cytosine (c) dna that is each dna molecule is comprised of two biopolymer strands coiling around each other to form a double. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a polymer of nucleotides linked together by specific bonds known as phosphodiester bridges. Dna base pairs — overview & structure. An a base on one strand will always. Iii according to the gels. Pairing involves specific atoms in each base. Adenine and thymine form two hydrogen for example, the e. Enzymes split the dna molecule into two strands and then transport corresponding nitrogenous bases to each strand. A nitrogenous base owes its basic properties to the lone pair of electrons of. The nitrogens have an extra lone pair that can be used up under the right conditions to potentially sop up and that's what actually forms the rungs of the ladder when these complimentary nitrogenous bases form. Enzymes link together to form a template for a new dna molecule to be built.
A nitrogenous base owes its basic properties to the lone pair of electrons of. Dna is the most important nucleic acids present in our body. The two strands are held together by h‑bonding between the bases (in anti conformation). Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. Not only are the nitrogenous bases located inside the double helix, but also they align with each other in a specific way.

Pairing involves specific atoms in each base.
Which pair of nitrogen bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? An a base on one strand will always. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases, with adenine forming a base pair with thymine, and cytosine forming a base pair with guanine. In a dna molecule, nitrogenous bases are of two types (3) in the interior of double helix, the nitrogenous bases of two polynucleotide strands form a pair with the help of hydrogen bonds. A nitrogenous base owes its basic properties to the lone pair of electrons of. The main biological function of a nitrogenous base is to bond nucleic acids together. Which pair of nitrogenous bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? This structure is very stable and it occurs because the dna base pairs are able to interact with other bases in a very specific pattern: According to chargaff's rule, a+g=c+t. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the. These five nitrogenous bases are all planar molecules, meaning that they are fairly flat and rigid. Adenine pairs with the thymine, and guanine pairs with 2. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
The number of base pairs varies between dna molecules. The nitrogenous bases stacked upon one another are spaced based on their van der waals distance. Rather, dna in bacteria is present in the form of a single large circular molecule within the center of the cell. The main biological function of a nitrogenous base is to bond nucleic acids together. The possibility of adenine=40% and.

Enzymes split the dna molecule into two strands and then transport corresponding nitrogenous bases to each strand.
Additionally, differences in nitrogenous base content of dna molecules and codon usage frequencies indicate segments of the genome with foreign origins. The main biological function of a nitrogenous base is to bond nucleic acids together. The two strands are held together by h‑bonding between the bases (in anti conformation). Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a polymer of nucleotides linked together by specific bonds known as phosphodiester bridges. Not only are the nitrogenous bases located inside the double helix, but also they align with each other in a specific way. Dna is composed of two strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonding. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. The base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; But this rule rule is applicable only for double stranded dna molecule. The double helix structure of the dna molecule places the four nitrogenous bases on the inside of the molecule. Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid which is a molecule that contains the instructions an there are 4 types of nitrogen bases adenine (a) thymine (t) guanine (g) cytosine (c) dna that is each dna molecule is comprised of two biopolymer strands coiling around each other to form a double. Which pair of nitrogenous bases will form a bond in a dna molecule? According to chargaff's rule, a+g=c+t.
Komentar
Posting Komentar